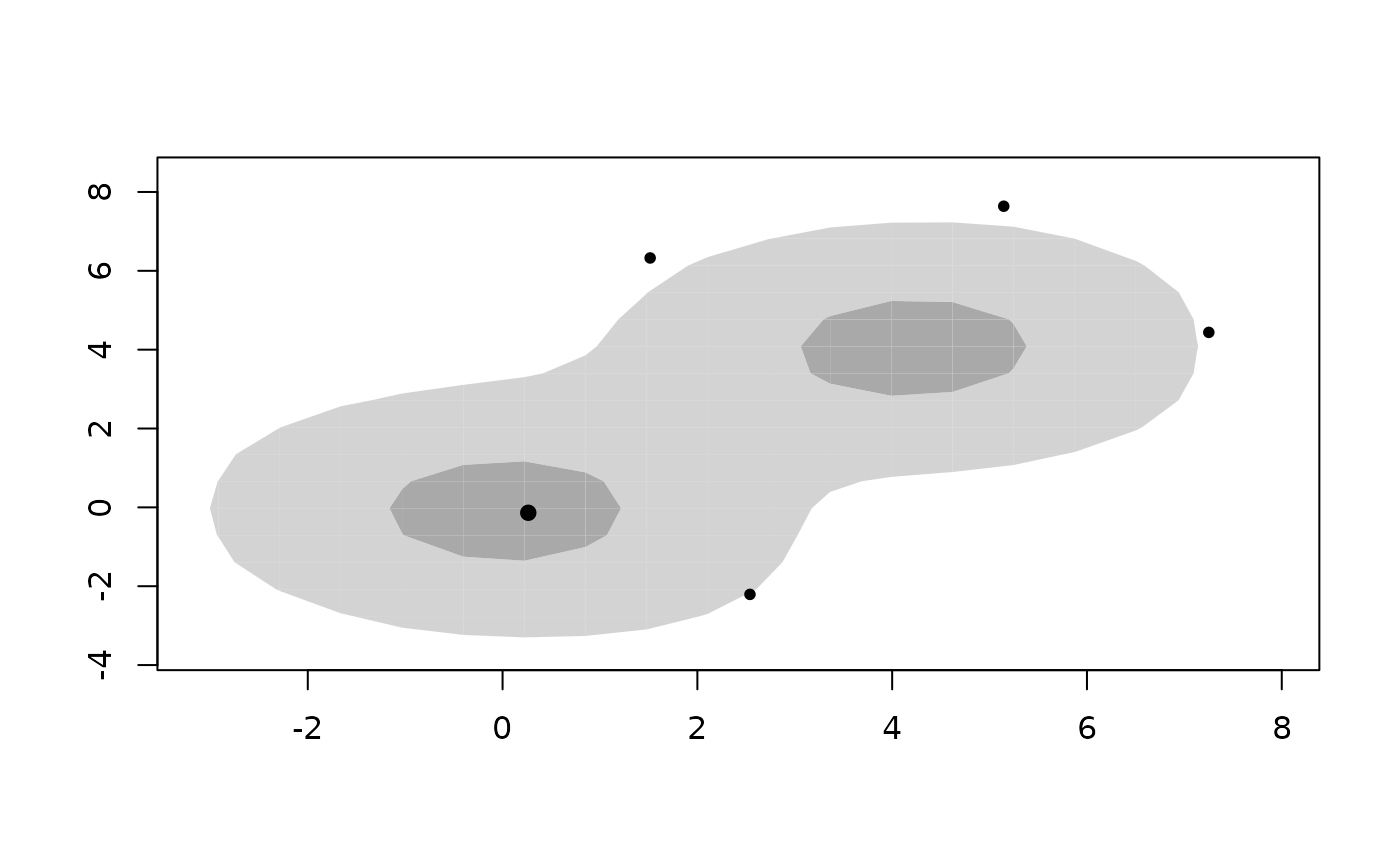
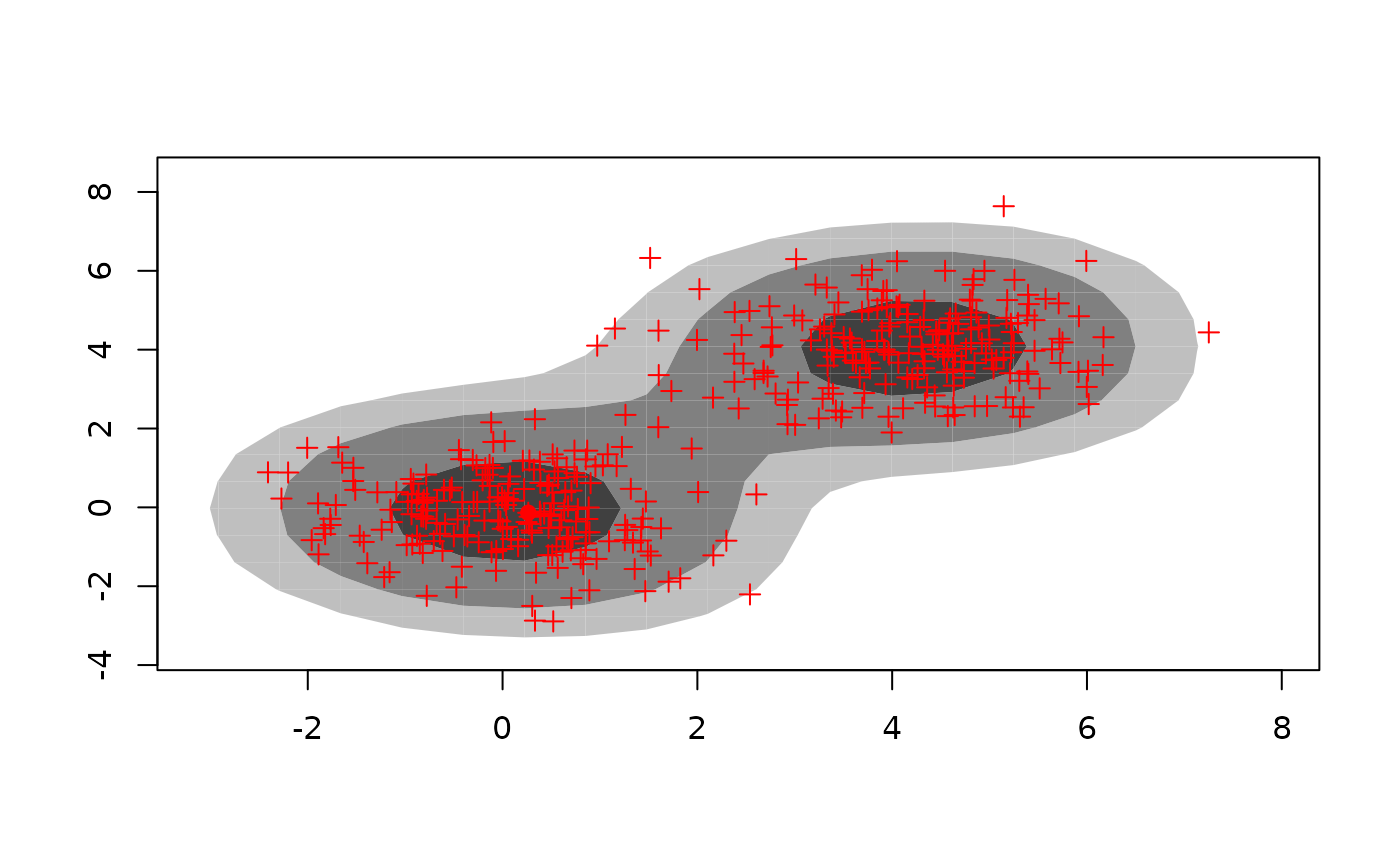
Calculates and plots highest density regions in two dimensions, including the bivariate HDR boxplot.
Usage
hdr.2d(
x,
y,
prob = c(0.5, 0.95, 0.99),
den = NULL,
kde.package = c("ash", "ks"),
h = NULL,
xextend = 0.15,
yextend = 0.15
)
hdr.boxplot.2d(
x,
y,
prob = c(0.5, 0.99),
kde.package = c("ash", "ks"),
h = NULL,
xextend = 0.15,
yextend = 0.15,
xlab = "",
ylab = "",
shadecols = "darkgray",
pointcol = 1,
outside.points = TRUE,
...
)
# S3 method for class 'hdr2d'
plot(
x,
shaded = TRUE,
show.points = FALSE,
outside.points = FALSE,
pch = 20,
shadecols = gray(rev(seq_along(x$alpha))/(length(x$alpha) + 1)),
pointcol = 1,
...
)Arguments
- x
Numeric vector
- y
Numeric vector of same length as
x.- prob
Probability coverage required for HDRs
- den
Bivariate density estimate (a list with elements x, y and z where x and y are grid values and z is a matrix of density values). If
NULL, the density is estimated.- kde.package
Package to be used in calculating the kernel density estimate when
den=NULL.- h
Pair of bandwidths passed to either
ash::ash2()orks::kde(). If NULL, a reasonable default is used. Ignored ifdenis notNULL.- xextend
Proportion of range of
x. The density is estimated on a grid extended byxextendbeyond the range ofx.- yextend
Proportion of range of
y. The density is estimated on a grid extended byyextendbeyond the range ofy.- xlab
Label for x-axis.
- ylab
Label for y-axis.
- shadecols
Colors for shaded regions
- pointcol
Color for outliers and mode
- outside.points
If
TRUE, the observations lying outside the largest HDR are shown.- ...
Other arguments to be passed to plot.
- shaded
If
TRUE, the HDR contours are shown as shaded regions.- show.points
If
TRUE, the observations are plotted over the top of the HDR contours.- pch
The plotting character used for observations.
Details
The density is estimated using kernel density estimation. Either
ash::ash2() or ks::kde() is used to do the
calculations. Then Hyndman's (1996) density quantile algorithm is used to
compute the HDRs.
hdr.2d returns an object of class hdr2d containing all the
information needed to compute the HDR contours. This object can be plotted
using plot.hdr2d.
hdr.boxplot.2d produces a bivariate HDR boxplot. This is a special
case of applying plot.hdr2d to an object computed using
hdr.2d.
References
Hyndman, R.J. (1996) Computing and graphing highest density regions American Statistician, 50, 120-126.