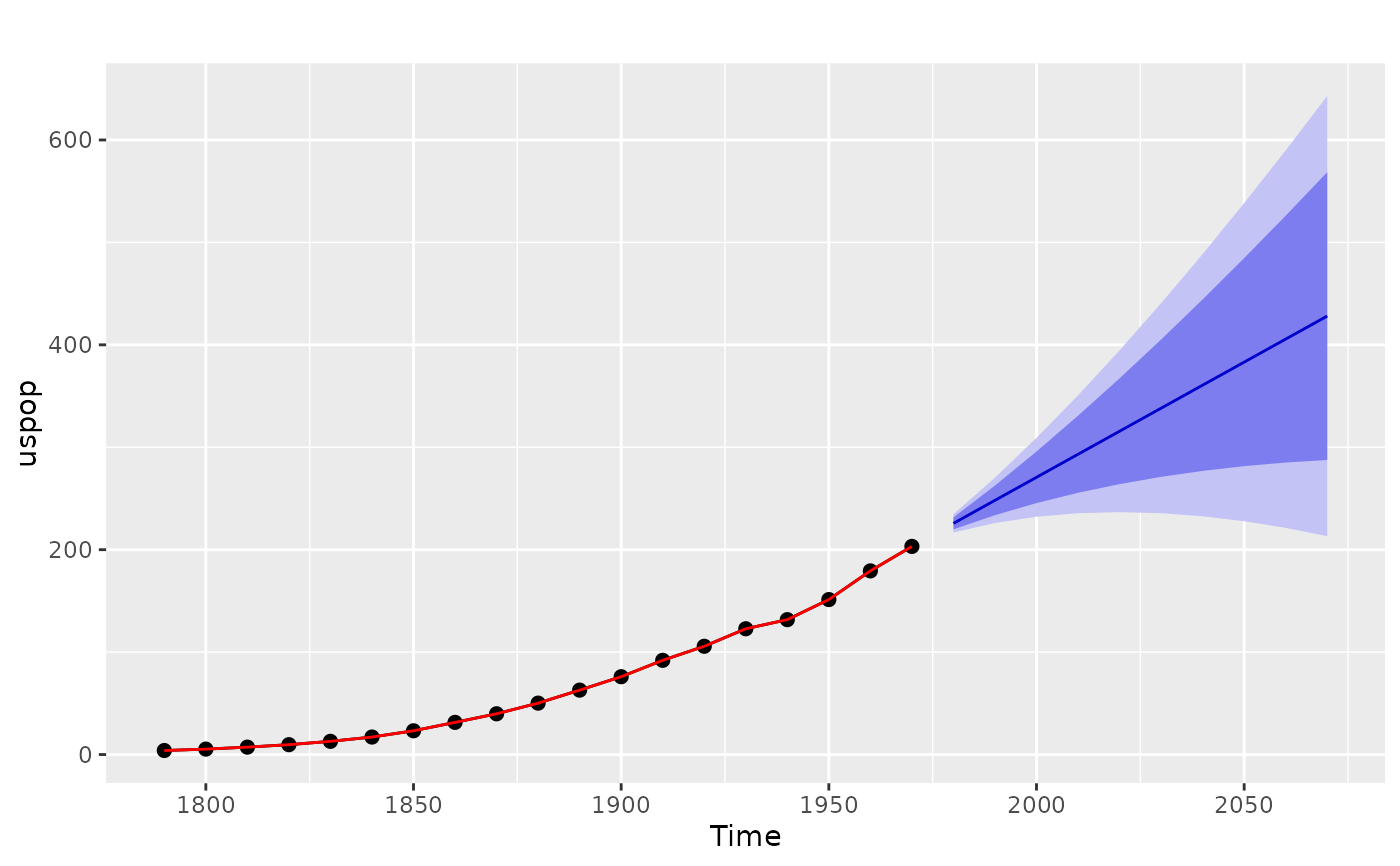
Fits a state space model based on cubic smoothing splines. The cubic smoothing spline model is equivalent to an ARIMA(0,2,2) model but with a restricted parameter space. The advantage of the spline model over the full ARIMA model is that it provides a smooth historical trend as well as a linear forecast function. Hyndman, King, Pitrun, and Billah (2002) show that the forecast performance of the method is hardly affected by the restricted parameter space.
Usage
spline_model(y, method = c("gcv", "mle"), lambda = NULL, biasadj = FALSE)Arguments
- y
a numeric vector or univariate time series of class
ts- method
Method for selecting the smoothing parameter. If
method = "gcv", the generalized cross-validation method fromstats::smooth.spline()is used. Ifmethod = "mle", the maximum likelihood method from Hyndman et al (2002) is used.- lambda
Box-Cox transformation parameter. If
lambda = "auto", then a transformation is automatically selected usingBoxCox.lambda. The transformation is ignored if NULL. Otherwise, data transformed before model is estimated.- biasadj
Use adjusted back-transformed mean for Box-Cox transformations. If transformed data is used to produce forecasts and fitted values, a regular back transformation will result in median forecasts. If biasadj is
TRUE, an adjustment will be made to produce mean forecasts and fitted values.
References
Hyndman, King, Pitrun and Billah (2005) Local linear forecasts using cubic smoothing splines. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Statistics, 47(1), 87-99. https://robjhyndman.com/publications/splinefcast/.